Scots pine
Scientific name:
Pinus sylvestris L.
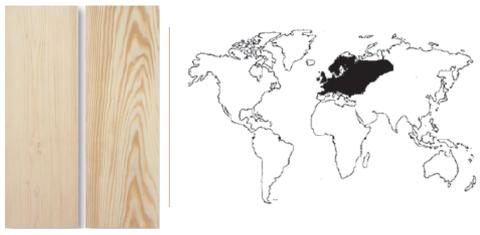
Geographic origin:
Asia and Europe.
- Sapwood: Light yellow
- Heartwood: Reddish colour
- Fiber: Straight
- Grain: from medium size to small size
- Characteristic defects: quite frequent lively small to large knots. Small resin bags.
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
y
z
Capacity of being impregnated
- Sapwood: Capable of being impregnated.
- Heartwood: Low capacity to no capacity of being impregnated.
Mechanical properties
- Resistance to static flexion 1,057 kg/cm2 &;8226; Elasticity module 94,000 kg/cm2
- Resistance to compression 406 kg/cm2
- Resistance to parallel traction 1,020 kg/cm2
Mechanization
- Sawing process: Easy and with no difficulties.
- Drying process: Easy and fast. Low risk of deformation and crack formation.
- Planing process: Easy.
- Gluing process: Easy.
- Nailing and screwing process: Easy.
- Finish: Easy
Physical properties
- Apparent density at 12% humidity 500 - 540 kg/m3 semi-light wood
- Dimensional stability
- - Volumetric contraction coefficient 0.38 % stable wood
- - Relation between contractions 1.81% medium tendency to deformity
- Hardness (Chaláis-Meudon) 1.9 Softwood to semi-softwood
Observations
- Fusta de creixement lent.
- A Gabarró anomenem paquets de flandes “curt” els paquets de llargs inferiors a L.3900. Els paquets de llarg 4200 en endavant els considerem “llargs”.
- Hi ha sectors o industrials que tenen alguna preferència pel que fa als llargs. Els fabricants de premarcs, per exemple, busquen llargs molt concrets, principalment L.4500 i L.5400.



