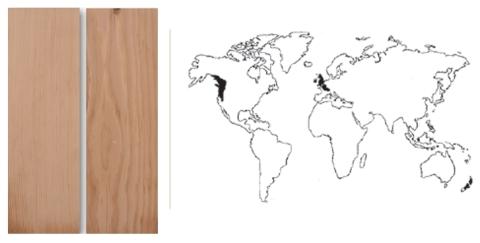
Douglas fir
Denominación científica:
Pseudotsuga menziessi Franco
Procedencia geográfica:
Northamerica (introduced in Europe, Australia, New Zeland)
- Sapwood: Pale shade yellow
- Heartwood: yellowish brown
- Fiber: Straight
- Grain: medium size to rough
- Characteristic defects: thick and adhesive Knots
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
y
z
Impregnabilidad
- Sapwood: From medium to low capacity of being impregnated
- Heartwood: No capable of being impregnated
Propiedades mecánicas
- Resistance to static flexion 860 kg/cm2 &;8226; Elasticity module 128,000 kg/cm2
- Resistance to compression 525 kg/cm2
- Resistance to parallel traction 930 kg/cm2
Mecanización
- Sawing process: Easy and with no difficulties
- Drying process: Easy. Low risk of crack formation.
- Planing process: Easy and with no difficulties
- Gluing process: Easy
- Nailing and screwing process: No difficulties. Resistance to be pulled away.
- Finish: No difficulties, although a blending agent should be applied in order to homogenize wood
Propiedades físicas
- Apparent density at 12% humidity
- 510 kg/m3 semi-light wood
- Dimensional stability
- - Volumetric contraction coefficient 0,41% stable wood
- - Relation between contractions 1,59% no tendency to deformity
- Hardness (Chaláis-Meudon) 2,45 Semi-softwood
Observaciones
- El color de la albura és molt diferenciat (del groc al vermell)



